1.Measuring the frequency spectrum of video transmission.
2.Determine the image carrier frequency range and sound carrier frequency.
3.Specifies the bandwidth on video transmission.
4.Specify the type of modulation on the picture and sound
Equipment Used:
1 Video modulator (VCD / VTR / video sender).
1 cable connector RCA- BNC.
Introduction:
How to transmit image signal which the amplitude is modulated similar to a radio broadcasting system that has been known.
In both cases, the amplitude of a carrier wave radio frequency (RF) is made varies with the modulating voltage. The modulation is a signal of fundamental frequency (baseband).
On television, this baseband signal is a composite video signal. Television broadcast is similar to a radio system, but includes pictures and sound.
Sound signal emitted by joining it in frequency modulation (FM) on a separate carrier wave transmitter in the same channel as the image signal.
This image signal means a modulated carrier wave.
The video signal is a signal for a picture tube. Video signal for the television audio is correspond to the sound system signal. Details for the AM image signal (amplitude modulation picture) and an FM voice signal.
Figure 2.a shows the frequency spectrum of video transmission that produces an image signal comprising AM picture carrier frequency (center frequency) and sound carrier frequencies (frequency side of the upper and lower side frequencies) - without VSB, while Figure 2b shows the frequency spectrum in transmission generate video image signals of AM frequencies only have the upper side only (with VSB).
A variation of DSB is used for broadcast TV. Under the FCC requirements, the standard video signal occupies a bandwidth of 4.5 MHz. The sound signal is separate and is transmitted at the upper edge of this signal. When carrier is shifted to bandpass, this one sided bandwidth becomes 9 MHz. This is nearly ten times as large as the total bandwidth occupied by all the channels of the AM radio. Use of SSB modulation would cut this in half but SSB is not used for video signals because of the complexity of the SSB receivers. TV manufacturers particularly American companies were instrumental in setting these standards like to keep the cost of the TV’s as low as possible so SSB receivers are not used.
This filter takes in a small part of the upper edge of the lower sideband, starting from -1.25 MHz. The signal is attenuated in this range from -1.25 MHz to -.75 MHz. From here on to 4 MHz, the signal is transmitted full strength. At 4 MHz it is once again attenuated down to 4.5 MHz so as not to interfere with the sound carrier which is demodulated separately. The shaded portion is what is transmitted.
The term vestigial is used since a tiny trace part of the lower sideband is also included in the transmission. The net result is that instead of transmitting a 9 MHz signal, we transmit only 6 MHz, the standard video signal today.
Unlike voice signals which have no components near the zero frequency, Video signals are very sensitive to their low frequency content. Distortion in these components degrades the picture. So extra care has to be taken to make sure that all the low frequency components (which are located in the center) are transmitted without distortion. VSB modulation transmits these low frequencies at the twice level. The motivation for filtering the signal in this way also comes from the desire to use a diode demodulator which requires an explicit carrier. But to recover the carrier we need to go a little to the other side of the carrier frequency and take in an attenuated part of the signal because of the limitations of practical filters. The development of this filter was a function of a compromise between bandwidth and the TV receiver complexity.
Lecture Video for Amplitude Modulation:
Experimental Procedure:
1.Calibrate the Spectrum Analyzer by determine the reference spectrum.
2.Set-up instruments just like in the picture above.
3.Turn ON the instrument.
4.Measure the video modulator output (RF) using the Spectrum Analyzer and observe the frequency spectrum.
5.Draw the frequency spectrum.
6.Determine how much is the images carrier frequency, voice carrier frequency, and the difference between.
7.Observe the spectrum, determine the type of modulation used in transmission by changing the SPAN FREQ (reduce the scale).
8. Draw the multiples frequency spectrum from it's frequency base.
Question:
1.What system is used in the video modulator?
2.From step 6, how do we know what types of modulation?
Experimental results:
Information | |
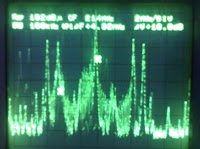
Ref = 102dBμ BW = 100 KHz CF = 5 MHz CP1ΔF + 4.32 MHz 2 MHz / DIV ΔV + 18.8 dB Image Carrier Frequency: LSB = 5 MHz - 4.32 MHz USB = 5 MHz + 4.32 MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be detected by the frequency spectrum analyzer because it's frequency very small | |
Ref = 102dBμ BW = 100 KHz CF = 214 MHz CP1ΔF + 4.32 MHz 2 MHz / DIV ΔV + 18.8 dB Image Carrier Frequency LSB = 214 MHz - 4.32 MHz USB = 214 MHz + 4.32 MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen by the spectrum analyzer because it's frequency very small | |
Ref = 102dBμ BW = 100 KHz CF = 421 MHz CP1ΔF + 4.32 MHz 2 MHz / DIV ΔV + 18.8 dB Image carrier frequency: LSB = 421 MHz - 4.32 MHz USB = 421 MHz + 4.32 MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen by the spectrum analyzer because it's frequency very small | |
Ref = 102dBμ BW = 100 KHz CF = 624 MHz CP1ΔF + 4.32 MHz 2 MHz / DIV ΔV + 18.8 dB Image Carrier Frequency: LSB = 624 MHz - 4,32 MHz USB= 624 MHz + 4,32 MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen by the spectrum analyzer because it's frequency very small | |
Ref = 102dBμ BW = 100 KHz CF = 831 MHz CP1ΔF + 4.32 MHz 2 MHz / DIV ΔV + 18.8 dB Image Carrier Frequency: LSB = 831 MHz - 4.32 MHz USB = 831 MHz + 4.32 MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen by the spectrum analyzer because it's frequency very small | |
BW = 100 KHz CF = 1055 MHz CP1ΔF + 4.32 MHz 2 MHz / DIV ΔV + 18.8 dB Image Carrier Frequency: LSB = 1055 MHz - 4.32 MHz USB = 1055 MHz + 4.32 MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen by the spectrum analyzer because it's frequency very small |
DATA ANALYSIS:
From the spectrum image that we get, we can know that the value of:
Carrier frequency: 421 MHz
CP1ΔF + 4.32 MHz
Then:
USB = 421 MHz + 4.32 MHz = 425.32 MHz
LSB = 421 MHz - 4.32 MHz = 416.68 MHz
Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen by the spectrum analyzer because it's frequency very smaller than the frequency carrier.
For the multiples frequencies:
- 1st multiple : 5 MHz
- 2nd multiple : 214 MHz
- 3rd multiples : 624 MHz
- 4th multiples : 813 MHz
- 5th multiples : 1055 MHz
Unlike voice signals which have no components near the zero frequency, Video signals are very sensitive to their low frequency content. Distortion in these components degrades the picture. So extra care has to be taken to make sure that all the low frequency components (which are located in the center) are transmitted without distortion.
QUESTION'S ANSWER:
- Modulation system that being use in the video are AMPLITUDE MODULATION, because the signal amplitude information affect the amplitude of the carrier signal, the signal information into the cover of the carrier signal.
Image Modulated Signal
A common use of signal Am is: AM radio broadcasting is widely used for broadcast AM radio wave signal, the TV image (Video), Radio communication: aircraft, amateur radio (SSB), CB radio (Citizens Band Radio). Digital data transmission: Modems Computers (combined with QAM modulation)
- This type of modulation is amplitude modulation and it can be seen from the changes in amplitude and has a spectrum of AM.
Based on the equation of the spectrum signal AM modulated, AM will have 3 (three frequencies):
- fc: carrier frequency signal
- LSB: Lower Side Band frequency (LSB), namely the difference between frequency carrier signal and the signal information.
- USB: Upper Side Band frequency (USB) is the addition of carrier signal frequency and signal information.
CONCLUSION
- Video modulator is using amplitude modulation (AM)
- AM modulation that shown on a spectrum analyzer displays are three frequencies namely
- Carrier frequency (fc)
- Lower Side Band Frequency (LSB)
- Upper Side Band Frequency (USB)
- The difference between USB and LSB frequencies are = 4.32 MHz
- Using 100 KHz bandwidth
Reference
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amplitude_modulation
http://elkakom.telkompoltek.net/
http://vodpod.com/watch/1793578-lecture-8-amplitude-modulation










Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar